See also Linux on Itanium#Debian
Debian 12 (sid)
Latest ISO: https://cdimage.debian.org/cdimage/ports/snapshots/2023-11-17/debian-12.0.0-ia64-NETINST-1.iso
Repository: https://snapshot-mlm-01.debian.org/archive/debian-ports/20240608T194259Z/
From mid 2019 until the end of 2023 some experimental builds of Debian were created and published on the Debian Ports website. While they were always rolling release, the ISO files carried the version numbers 10 - 12, with the latest version identifying itself as "trixie" after installation, the codename of Debian 13. For simplicity, this section will call it Debian 12 anyway.
Development effectively ended on 9 June 2024 with the architecture being removed from the Debian Ports website. This was justified with end of upstream support for the architecture. The repositories have been partially removed and can now only be accessed using the Snapshots archive.
Freezing issues
This build of Debian does not boot reliably on every machine. It most commonly crashes at these steps:
- Stuck on
random: crng init done - Stuck on
Timed out waiting the udev queue being empty - Stuck on an endless CPU watchdog timeout
- Booting to a BusyBox environment because the HDD could not be loaded
If you actually get a login prompt, boot has succeeded. Sometimes early during boot though some drivers may have crashed though so check dmesg if any errors happened during boot.
On an rx2600 my personal experience is that roughly 2/3 of boots fail or encounter at least an error. Sometimes the system kernel panics after a few minutes of uptime. Thus it is strongly recommended to only reboot the machine when the machine has a working Management Card or someone can physically reset the machine if it should fail to come back up.
Mitigations
- Add
hardened_usercopy=offas a boot parameter, both during installation and later when using the system - Add
modprobe_blacklist=radeon nomodesetas boot parameters if you use an ATI GPU
Repositories
Now that the archive repository is gone, there is only the snapshot left. The guide below shows how to use it for apt, however note that it is rather slow and sometimes temporarily blocks connections from an IP if too many files are downloaded too quickly. I'm working on mirroring that mirror to make this process easier.
Installation
1. Boot the installation
The ISO linked above can either be burned to a CD or DVD, or it can be extracted onto a FAT32 formatted USB drive. Booting is possible by launching EFI\boot\bootia64.efi from the EFI shell or the boot menu.
Due to some instabilities in the Kernel it is recommended to add a boot flag to the GRUB commands of the installation. Once GRUB is launched, press E to open the editor and modify the following line:
linux /install/vmlinuz --- quiet hardened_usercopy=offBoot by pressing F10. If the boot process freezes, try again.
2. Installing Debian
From here installing should be straight forward. Follow the instructions and set your preferences. When it comes to formatting the HDD, it is recommended to use the guided partitioning. If you don't want to do this, make sure to create an EFI partition that mounts to /boot/efi.
During setup you might see some access error pop up on the screen, these can usually be ignored.
Once setup is finished, you can reboot. However we are not done yet.
3. Repairing the installation
You will likely notice that no new boot entry was created for Debian. Right now this does not matter, it would not boot anyway due to a broken ISO.
Boot again into the Installation CD/USB, this time selecting the Recovery mode. Make sure to add the boot flag mentioned before, which should look like this:
linux /install/vmlinuz rescue/enable=true --- quiet hardened_usercopy=offBoot by pressing F10. And also here if booting does fail, try again.
Once booted, set your preferences and make sure to set up networking. Afterwards launch a shell in the new installation. The installer will ask you to select the partition, it usually is either /dev/sda2 or /dev/sdb2. Once you are in the shell, edit the file /etc/apt/sources.list to make it look like this:
deb [trusted=yes] http://snapshot-mlm-01.debian.org/archive/debian-ports/20240608T194259Z/ sid main contrib non-free non-free-firmware
If the file contains an entry for the CD, remove it.
Afterwards fully update the system with apt update and apt upgrade. This will install a non-broken version of GRUB and update the kernel to a more reliable version.
Once the update process has completed, edit the file /etc/default/grub to make sure that the following boot parameters are set:
GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX="hardened_usercopy=off modprobe_blacklist=radeon nomodeset"If your system does not have an ATI GPU, you can remove the modprobe and nomodeset entries. Complete the process by running update-grub. Afterwards reboot.
4. Finally booting
Now you can boot the system normally by launching EFI\boot\bootia64.efi. You can also create a boot entry for this file to make booting easier.
Known issues
- The only tasksel items that can be installed are SSH server and laptop
- The only desktop environment that can be installed is
xfce4which is missing some standard software that would come with the tasksel variant
- The only desktop environment that can be installed is
- The following packages are known to be broken:
- btop
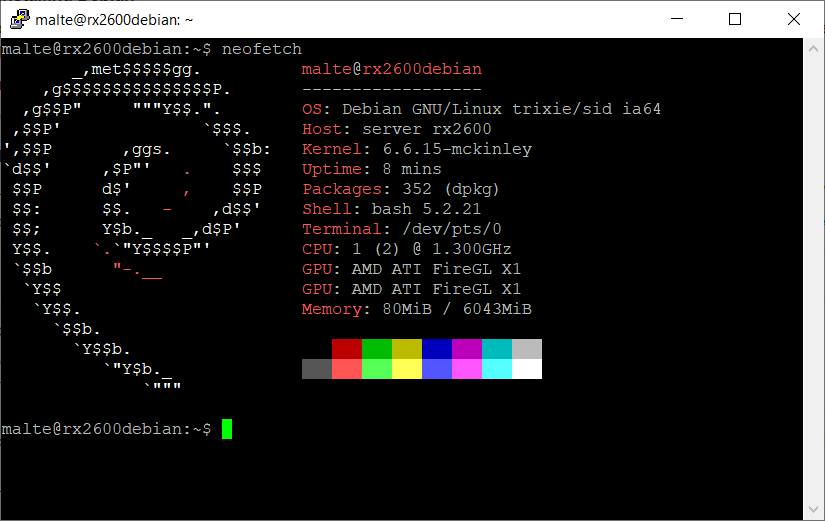
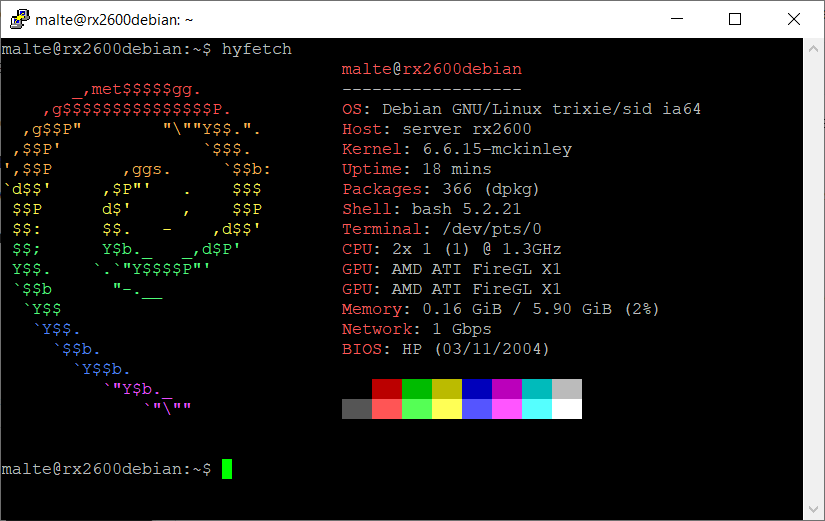
Screenshots
-
Neofetch
-
Hyfetch